The True Protein Digestibility of normal maize and Quality Protein Maize is almost same, but the biological value of normal maize is just half as compared to that of QPM varieties (Young et al 1971). Rather, the biological value of QPM is highest among all the food grains (Figure 1) owing to the reason that all cereals except QPM are deficient in lysine, an essential amino acid and all pulses are deficient in methionine, the other essential amino acid (Yadavn et al, 2008). The quality parameters viz., protein content, lysine & tryptophan content of QPM hybrids released for their cultivation in India are given in Table 3.
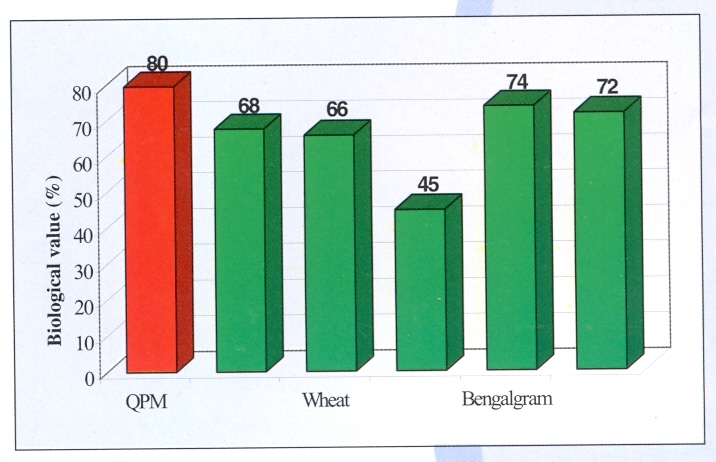
Figure 1 Biological value of QPM in comparision to other cereals and pulses